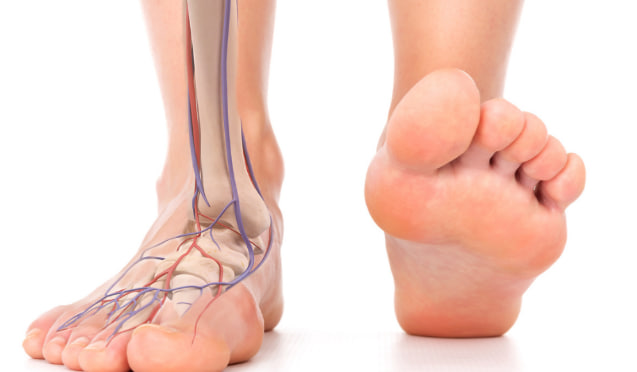
As people age, it is common to experience changes in the way their legs and feet feel. Coldness, numbness, tingling, swelling, or a sensation of heaviness in the lower limbs can signal reduced blood circulation. According to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), circulation problems in the legs may be linked to conditions such as peripheral artery disease (PAD), diabetes, or prolonged periods of inactivity.
While medical evaluation and lifestyle adjustments are essential, certain nutrients—especially Vitamin B3 (niacin)—play an important role in supporting healthy blood flow. When combined with other vitamins and healthy habits, they can contribute to better vascular function and comfort in the lower extremities.

Understanding Poor Circulation in the Legs
Poor circulation means that blood is not moving efficiently through the arteries and veins, reducing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to tissues. This can result in:
-
Cold or numb feet and toes
-
Tingling sensations
-
Swelling in the ankles or calves
-
Fatigue or heaviness in the legs
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes that underlying causes may include narrowed arteries from plaque buildup, chronic conditions like diabetes, or sitting for extended periods without movement.
Vitamin B3 (Niacin) and Blood Flow
Vitamin B3, also known as niacin, is a water-soluble vitamin that helps the body convert food into energy and supports cardiovascular health. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), niacin has several effects that may benefit circulation:
-
Vasodilation – Niacin can help blood vessels widen, which may promote smoother blood flow in narrowed arteries.
-
Cholesterol Management – Niacin supports healthy cholesterol balance by lowering LDL (“bad” cholesterol) and triglycerides while raising HDL (“good” cholesterol). Healthy cholesterol levels can help reduce plaque buildup in blood vessels.
-
Endothelial Function – Niacin supports the lining of blood vessels, called endothelial cells, helping them function efficiently in regulating blood flow and blood pressure.
Some individuals may experience a “niacin flush” after taking supplements—a temporary warming or tingling sensation. The NIH Office of Dietary Supplements reports that this effect is generally harmless, though high doses should only be taken under medical supervision.
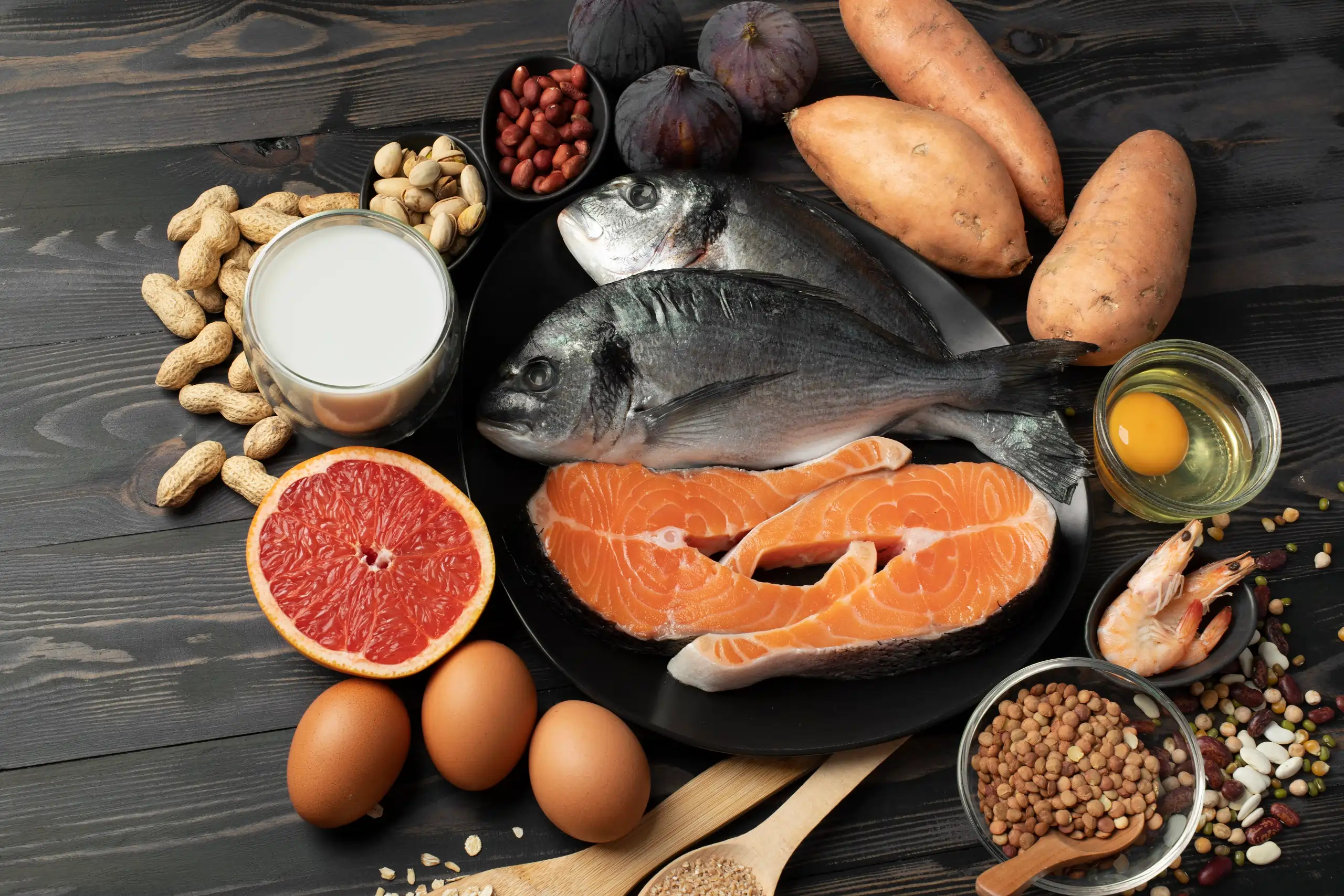

Other Essential Vitamins for Circulatory Health
While niacin is noteworthy for its role in vascular function, other vitamins also support healthy blood circulation:
1. Vitamin E – Antioxidant Support for Blood Vessels
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that helps protect cells from oxidative stress. The NIH notes it plays a role in maintaining the integrity of blood vessels and preventing clumping of platelets, which supports smoother blood flow.
Food sources: sunflower seeds, almonds, spinach, and avocado.
2. Vitamin C – Collagen Production and Vessel Strength
Vitamin C aids in collagen synthesis, which is vital for maintaining strong, flexible blood vessel walls. The Linus Pauling Institute explains that Vitamin C also reduces inflammation, which can contribute to arterial stiffness.
Food sources: oranges, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli.
3. Vitamin D – Supporting Vascular Function
Vitamin D, often called the “sunshine vitamin,” helps regulate blood pressure and may influence arterial health. Research published in Circulation has linked low Vitamin D levels to increased arterial stiffness.
Food sources: fortified dairy products, eggs, fatty fish such as salmon and sardines, and moderate sun exposure.
4. Vitamin B12 – Red Blood Cell Production
Vitamin B12 is crucial for producing healthy red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. A deficiency can lead to anemia, resulting in fatigue and reduced oxygen delivery to the legs.
Food sources: eggs, dairy, beef liver, clams, and fortified cereals.
Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs)
According to the NIH, the RDAs for these vitamins for most adults are:
-
Vitamin B3 (Niacin): 14–16 mg
-
Vitamin E: 15 mg
-
Vitamin C: 75–90 mg
-
Vitamin D: 600–800 IU
-
Vitamin B12: 2.4 mcg
These amounts can generally be met through a balanced diet. Supplementation may be recommended for individuals with deficiencies, but should be guided by a healthcare professional.

Dietary Sources of Circulation-Supporting Vitamins
Incorporating nutrient-rich foods is an effective way to support vascular health naturally:
-
Niacin: chicken, turkey, salmon, tuna, brown rice, peanuts, lentils
-
Vitamin E: sunflower seeds, almonds, spinach, avocado
-
Vitamin C: citrus fruits, strawberries, kiwi, bell peppers, tomatoes
-
Vitamin D: fortified milk, eggs, fatty fish, sun exposure (with skin protection)
-
Vitamin B12: dairy products, eggs, lean meats, fortified cereals
Lifestyle Habits to Improve Circulation
While nutrition is important, circulation also depends heavily on lifestyle factors. The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends:
-
Regular Physical Activity – Walking, swimming, or cycling helps strengthen the cardiovascular system.
-
Leg Elevation – Elevating the legs above heart level can reduce swelling and aid venous return.
-
Adequate Hydration – Staying hydrated helps keep blood from becoming too viscous.
-
Frequent Movement – Avoid sitting or standing in one position for long periods; take short movement breaks.
-
Compression Garments – Compression socks can help promote venous blood flow in the lower legs.
-
Smoking Cessation – Smoking damages blood vessels and impairs circulation.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Persistent symptoms such as cold feet, unexplained swelling, frequent numbness, or pain in the legs should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. These signs may indicate PAD, blood clots, or other vascular conditions that require treatment.
Before starting supplements—particularly niacin in higher doses—individuals should consult their doctor, especially if they have existing heart disease, high cholesterol, diabetes, or are taking medications.