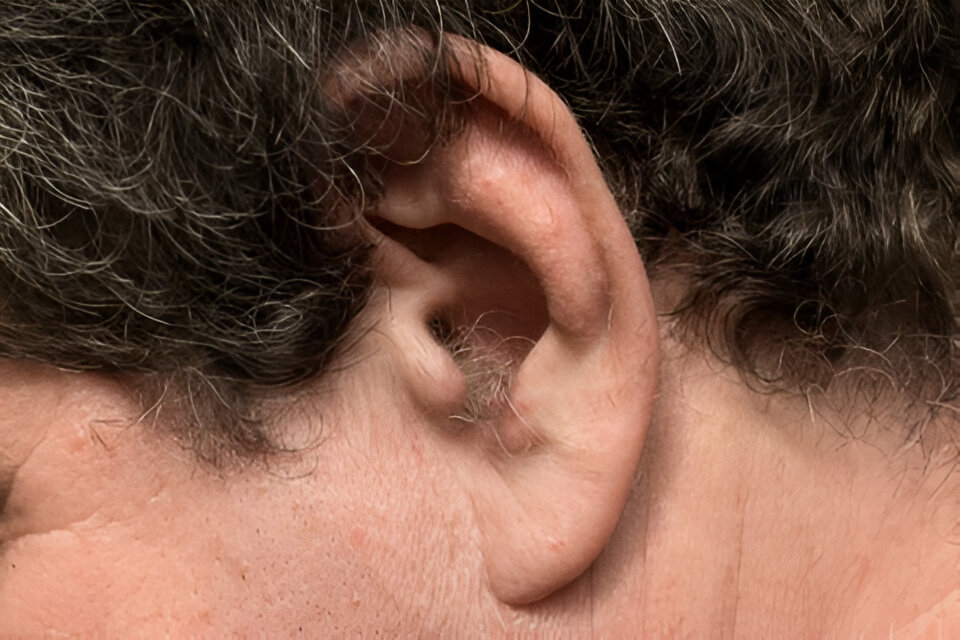
Ear hair can be a perplexing topic, especially as it becomes more noticeable with age. If you’ve ever wondered why these hairs appear, how they impact your health, or how to manage them, you’re in the right place. In this article, we’ll dive into the causes of ear hair growth, its function, and what you can do if you wish to manage it.
What Causes Ear Hair Growth?
The appearance of ear hair is primarily linked to hormonal and genetic factors. One of the primary hormones involved in this process is dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is a powerful derivative of testosterone that can increase as we age, particularly in areas of the body where hair growth was either sparse or absent. As DHT levels rise, it stimulates hair follicles in places such as the ears, resulting in the growth of thicker, coarser hairs.
Genetics also play a significant role in ear hair development. If you have family members who experience hair growth in the ears, there’s a higher likelihood that you’ll have it too. It’s a hereditary trait that often manifests in adulthood.
An additional medical term you might come across is auricular hypertrichosis, which refers to excessive hair growth in the ear region. This condition is more commonly observed in older men but can also affect younger individuals, particularly those with a genetic predisposition. Interestingly, auricular hypertrichosis is more prevalent in certain ethnic groups, including individuals of Indian descent, where it is sometimes considered a hereditary feature.
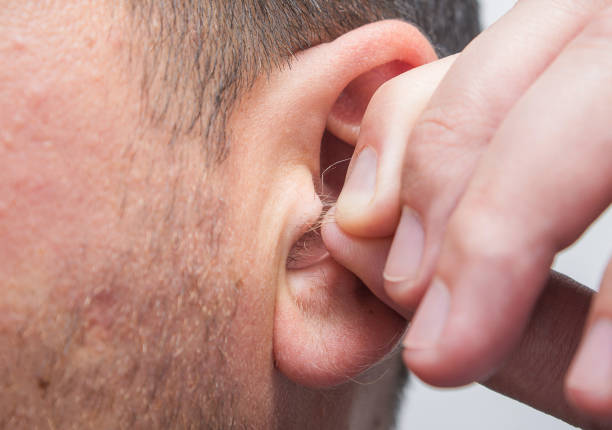
Is Ear Hair Dangerous?
In most cases, ear hair is completely harmless. It may seem like a trivial concern, but these tiny hairs actually serve an important function. They act as a barrier, preventing dust, insects, and other small particles from entering the ear canal. This natural protection helps maintain ear hygiene and contributes to overall ear health.
However, there are instances when ear hair can become problematic. If there is an excessive amount of hair, it may obstruct proper cleaning of the ear canal, making it more difficult to maintain hygiene. This could, in rare cases, increase the risk of infections or ear discomfort. But again, ear hair in and of itself is not a cause for medical alarm.
Auricular hypertrichosis, while not dangerous to health, can have aesthetic implications. For individuals who feel self-conscious about the appearance of ear hair, it can be an unwelcome feature. It’s essential to distinguish between typical ear hair and cases where the growth may signify an underlying issue that needs medical attention.
If ear hair growth is accompanied by additional symptoms such as pain, unusual discharge, or hearing loss, it’s crucial to seek advice from a healthcare professional to rule out any potential problems.
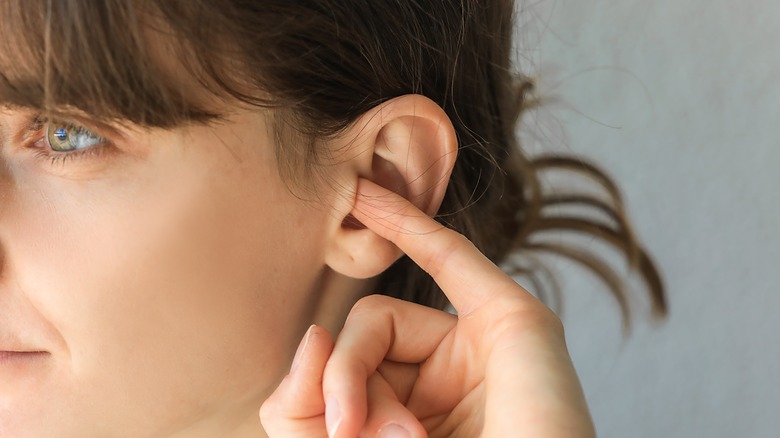
How to Manage Ear Hair?
If you prefer to remove or trim your ear hair for cosmetic reasons or personal comfort, several options are available. Each method comes with its pros and cons, and it’s essential to choose the one that best suits your needs:
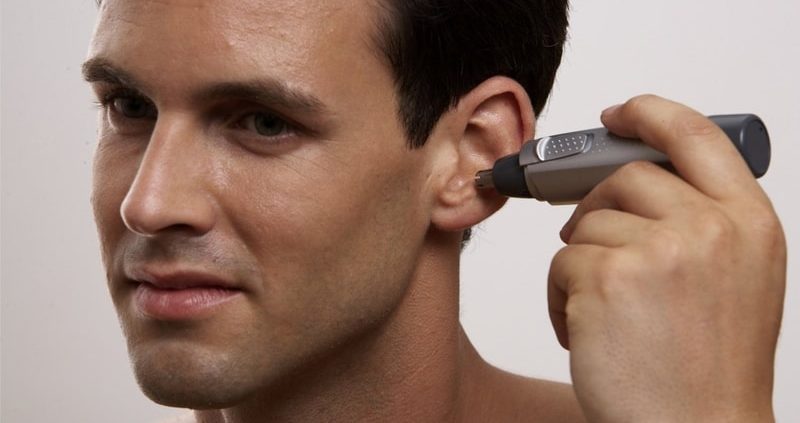
1. Electric Trimmers
Electric trimmers designed specifically for the ears are one of the safest and most convenient ways to trim ear hair. They are gentle on the sensitive skin of the ear and allow you to quickly manage unwanted hair without risk of cuts or nicks.

2. Laser Hair Removal
For those seeking a more permanent solution, laser hair removal offers a long-lasting approach. Although it typically requires multiple sessions and should be done by a trained professional, it can significantly reduce hair growth in the ear area over time.
3. Manual Tweezing
For a more targeted approach, some individuals opt to tweeze ear hair manually. However, this can be a more time-consuming method and might not be suitable for large areas of ear hair.
Before choosing any hair removal method, it’s always a good idea to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice and help ensure you select the best option for your skin and hair type.
4. Waxing or Depilatory Creams
Waxing and depilatory creams are also options for removing ear hair. While these methods can be effective, they should be used cautiously, as they can irritate or damage the sensitive skin of the ear. Always perform a patch test before using these products on the ear area to avoid unwanted reactions.
Fun Facts About Ear Hair
- Cultural Associations: In some cultures, ear hair is considered a sign of wisdom and maturity, symbolizing the aging process and the accumulation of life experience.
- Hormonal Changes: Studies suggest that the increase in ear hair may be linked to hormonal shifts that occur as we age. This could be a sign of changes in testosterone or other hormones, which affect hair growth patterns in various parts of the body.
- Ethnic Variations: Some ethnic groups are more prone to developing ear hair due to genetic factors. For example, individuals of South Asian descent may experience more significant ear hair growth due to hereditary traits.
Conclusion
While ear hair might seem like an insignificant detail, it actually has a biological purpose and plays a protective role in keeping the ear canal clean. Generally, it’s not a cause for medical concern unless excessive hair growth interferes with ear hygiene or causes discomfort. There are various ways to manage ear hair, whether for aesthetic reasons or comfort, and consulting a specialist can help you find the most suitable solution.
Ultimately, ear hair is a normal part of the human experience, and whether you choose to manage it or leave it, understanding its causes and functions can help you feel more informed and comfortable.
Sources: